Research provides an analysis of the field effectiveness of 15 original equipment manufacturer (OEM) active safety and advanced headlighting systems
Nationwide, United States
Analysis of the Field Effectiveness of General Motors Production Active Safety and Advanced Headlighting Systems
Summary Information
For this study, General Motors partnered with the University of Michigan Transportation Research Institute (UMTRI) to understand the real-world effectiveness of 15 original equipment manufacturer (OEM) active safety, driver assistance, and advanced headlighting features that may prevent or mitigate different types of crashes.
This analysis included VIN-linked data on 3,785,419 vehicles across 22 vehicle models (including Buick, Cadillac, Chevrolet, and GMC) and five Model Years (Model Year 2013-2017). For each vehicle (or VIN) in the dataset, the presence or absence of the various safety systems examined was provided by the OEMs. These systems break down into categories aimed at addressing rear-end striking (or front-to-rear) crashes, lane departure crashes, lane change crashes, backing crashes, and low visibility nighttime crashes.
The safety system content data of the 3.7 million vehicles was matched to police-report data from vehicles involved in crashes using 10 state crash databases that provided full 17-character VINs for the vehicles involved. Using "quasi-induced exposure" methods, comparisons of "system-relevant" crash counts and "control" crash counts for equipped and unequipped vehicles were used to estimate the safety systems' effectiveness. Control crashes served to control for vehicle exposure and were selected to be unaffected by the system examined. Logistic regression statistical methods were utilized for field effectiveness estimation, which adjusted for other factors such as weather, road type, and driver age and gender.
Findings
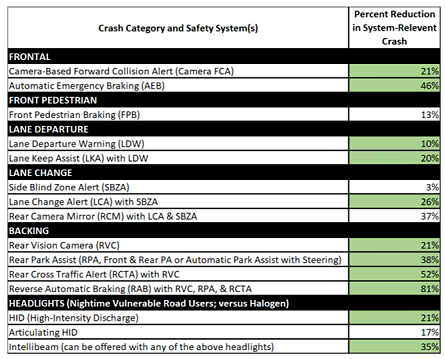
The results show that several of these features are making a statistically significant impact in helping to reduce crashes (see table below).
Table: Estimated percent reductions in system-relevant crashes for various OEM active safety and advanced headlighting systems